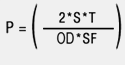|
|
| Home | About Us | Product | Application | Technical | Contact Us | EN | ES | FR | IR | AR | RU | |
| Pressure Calculation | |
Tubing specifications do not include any recommended service or burst pressure requirements. However, Barlow's formula is commonly used in the industry to approximate or predict the bursting pressures of ductile thin wall tubes. Working pressures or allowable pressures are calculated by using a safety factor (SF) to reduce the pressure from a level where bursting failure is very likely to an acceptable level of risk. This is a complex matter where many issues must be considered such as: personnel assessment and general safety, corrosion, fatigue, fabrication changes (bends, flares), codes and insurance, seismic stability and temperatures, to name a few. Barlow's formula can be used to estimate burst pressure of tubes. |
|
| Home | About Us | Product | Application | Technical | Contact Us | EN | ES | FR | IR | AR | RU | |